Code Development Outline and Begin Coding
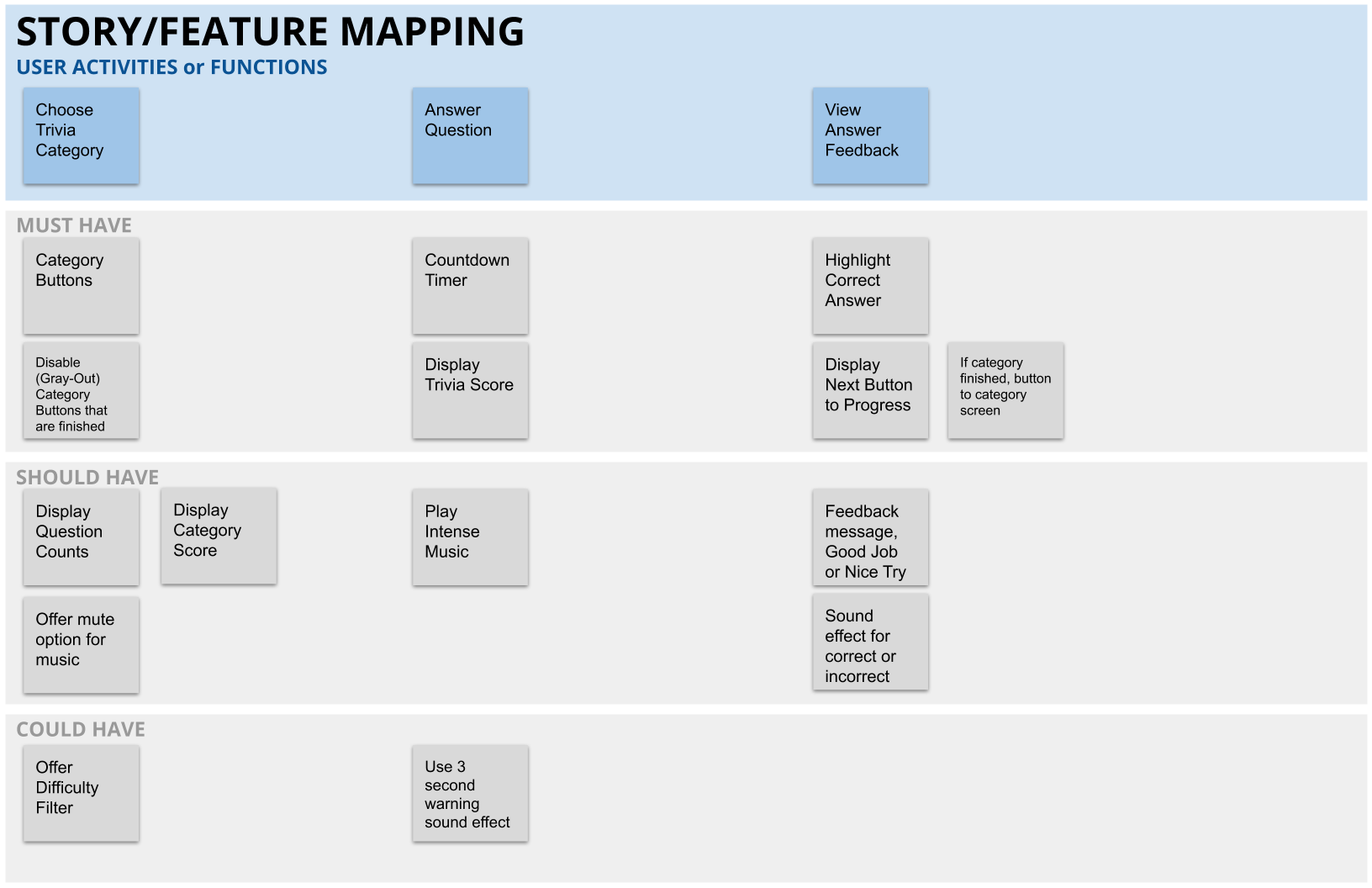
Outline the features to program by priority--core features, enhanced features, and wish list features. You will find an example of a basic requirements document in the examples tab, as well as the feature map example that can serve the same purpose. Begin coding and maintain well organized code as you progress towards your first full demonstration. It is important to code in "chunks" that you can test frequently to minimize the chance of some bugs getting very hard to diagnose.
Optionally, you could use pseudocode to outline your plan for development as well. This Kahn Academy tutorial is a good introduction to the technique.
❏ Deliverable A document or slide that outlines your progressive development plan.

✓- Below Standard
✓ At Standard
✓+ Above Standard
A prototype is provided but lacks detail to make the evaluation fruitful, not demonstrating a unique visual or interactive perspective on the basic trivia template design.
A prototype that demonstrates thoughtful concept design and provides a good representation of idea for feedback from participants.
A prototype that is exceptional in representing and evaluating some novel concepts in an efficent way for participants, or a couple variations of a prototype are presented to test alternate concepts.
An evaluation is presented but doesn't communicate any added value to the team's development process.
An evaluation that produces valuable insights on improving and developing the team's concept.
An evaluation that is exhaustive and thoughtful in collecting as much useful information from participants while be respectful of their time.
A marketing card is complete but is very basic and lacks cohesion with the overall team's project.
A marketing card conveying a consistent visual and narrative story with the game concept that will clearly generate interest in the game.
A marketing card with an exceptionally engaging and visual message to try the trivia game.